Mrs Kell, a 45 year old homemaker complains of dysphagia to liquids and solids for some years. Endoscopy showed:
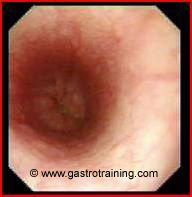
What is the diagnosis?
The picture shows a normal oesophagus. Oesophageal biopsies should be obtained to exclude eosinophilic oesophagitis.
Discuss the next steps?
Dysphagia to liquids in the absence of any oesophageal obstruction is strongly suggestive of a motility disorder. Options:
Oesophageal manometry- if available is ideal, particularly if achalasia is suspected
Barium swallow- is reasonable if achalasia is unlikely form the clinical history. The diagnostic accuracy of barium swallow for achalasia is approximately 95 percent.
Discuss oesophageal motility disorders?
Oesophageal dysmotility is defined as motility that differs significantly from accepted normal variations. The clinical significance of this is unknown. With the exception of achalasia, the relationship between the manometric patterns and clinical symptoms remain controversial. Oesophageal dysmotility could be primary or secondary to systemic diseases like scleroderma, diabetes, Chagas disease, chronic GORD and chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo obstruction.
Discuss the clinical features of oesophageal dysmotility?
Dysphagia and chest pain
Classify oesophageal motility disorders?
3 types- hypercontracting, hypocontracting, and discoordinated motility besides achalasia. Hypocontracting motility disorder may be caused by GORD.
There is no definite treatment for oesophageal motility disorders except for achalasia.
What are the endoscopic features of achalasia?
- Normal in 40% of patient. There may be residual food in a dilated oesophagus
- Evidence of local inflammation may be there.
- Might find resistance while passing the GOJ
- Oesophagus may be dilated, elongated and tortuous( like colon)
Discuss the clinical features of achalasia?
- Men and women are affected with equal frequency.
- The disease can occur at virtually any age, but onset before adolescence is unusual.
- Dysphagia for solids and liquids is the primary clinical feature of achalasia
- Dysphagia for liquids is most characteristic of achalasia and strongly suggests the diagnosis.
- Difficulty belching is present in approximately 85 percent of patients. Few describe this symptom spontaneously.
- Weight loss, regurgitation, chest pain, and heartburn can occur. Regurgitation of material at night may result in aspiration.
- GORD symptoms occurs with surprising frequency in achalasia – probably by direct inflammation of the mucosa by the food, pills, or lactate production by bacterial fermentation of retained carbohydrate.
Further reading
Achalasia, Oesophageal dysmotility, Achalasia dilatation, Botox injection