Endoscopic injection of BOTOX in motility disorders
The module covers:
- What is BOTOX
- When to use BOTOX
- How to make up the solution and ready the device
- How to actually use it once it is set up
What is BOTOX
BOTOX contains Clostridium botulinum type A neurotoxin complex.
Botulinum toxin injected into the Lower Oesophageal Sphincter (LOS) of patients with achalasia/or pylorus poisons the excitatory acetylcholine-releasing neurons thereby producing a therapeutic decrease in LOS/pylorus pressure
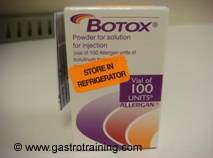
Picture1: BOTOX Allergan 100units, powder for solution for injection Containing Clostridium botulinum type A neurotoxin complex
When to use BOTOX
- Achalasia- ONLY TO treat elderly or infirm patients for whom pneumatic dilation and surgical myotomy has unacceptable risks. The long-term safety and efficacy remain uncertain
- Gastroparesis- not very good evidence.
How to make up the solution and ready the device
- Equipments
- Injector needle
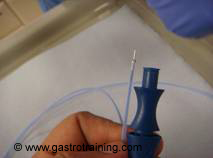
Picture2: Injector needle - Botox (100units)
- 2ml syringe to calculate needle volume
- 5ml syringe to draw up after Botox powder has been diluted
- Injector needle
- Dose:
- Achalasia: 100 units (25units in four sectors) in the GOJ
- Gastroparesis (idiopathic or diabetic): 100 units (25units in four sectors) in the pylorus
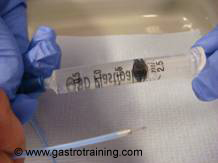
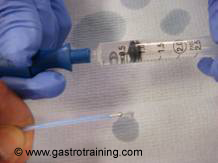
Picture3 and 4: Needle volume is 2ml-1ml=1ml
- Making up the BOTOX
- The botox in the vial is almost invisible
- To determine how much water to dissolve it into first determine the volume of normal saline you need to prime the injection needle
- Standard injection needle volume is 1ml ( as shown above to see the water drop from the tip you push from 2ml to 1ml)- but always check your needle dead space volume before actual start
- Then inject 4ml of NS into the vial and gently swirl it without agitation (agitation inactivates botox) and withdraw it into the 5ml syringe.
- Each ml=25units
- If your needle volume is more say 1.5ml then dissolve the powder with four times the needle volume so that one fourth of the solution will have 25units
How to actually use it once it is set up
- These patients are prone to aspirate particularly when regurgitation of old food is the predominant symptom.
- The patient is advised to fast for at least 12 hours prior to the procedure +/- liquid diet for one or two days preceding the injection
- After the completion of diagnostic OGD come back to GOJ
- It is easier to inject on a retroflexed view ( J manoeuvre in the fundus)
- Prime the injection needle with 1ml of Botox solution
- When ready say ‘advance needle’ and then Inject 1ml =25U in sector 1 and when finished say ‘ needle back’
- Similarly inject in sector 2 and 3
- In sector 4 inject 1ml of NS which will push the remaining Botox from the injection needle channel.
- For treatment of gastroparesis inject 25 units in 4 sectors in the pylorus.
- Make sure the needle is in the muscle layer rather than submucous layer.
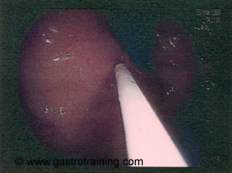
Picture6: Fundal retroflexed view:Actual injection needle in use
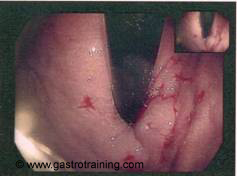
Picture5: After the GOJ injections
Acknowledgement/Bibliography:
- Storr M et al.Treatment of achalasia: the short-term response to botulinum toxin injection seems to be independent of any kind of pretreatment. BMC Gastroenterol. 2002; 2: 19.
- Pasricha PJ et al. Intrasphincteric botulinum toxin for the treatment of achalasia. N Engl J Med. 1995 Mar 23;332(12):774-8.
- Fishman VM et al. Symptomatic improvement in achalasia after botulinum toxin injection of the lower esophageal sphincter. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 Sep;91(9):1724-30.
- Product guide of the respective companies- Allergen